SUPPORT TRACK THE TROPICS
Over the last decade plus if you appreciate the information and tracking I provide during the season along with this website which donations help keep it running please consider a one time... recurring or yearly donation if you are able to help me out...
Venmo: @TrackTheTropicsLouisiana
Website: TrackTheTropics.com/DONATE
Venmo: @TrackTheTropicsLouisiana
Website: TrackTheTropics.com/DONATE
Track The Tropics is the #1 source to track the tropics 24/7! Since 2013 the main goal of the site is to bring all of the important links and graphics to ONE PLACE so you can keep up to date on any threats to land during the Atlantic Hurricane Season! Hurricane Season 2026 in the Atlantic starts on June 1st and ends on November 30th. Do you love Spaghetti Models? Well you've come to the right place!! Remember when you're preparing for a storm: Run from the water; hide from the wind!
Tropical Atlantic Weather Resources
- NOAA National Hurricane Center
- International Meteorology Database
- FSU Tropical Cyclone Track Probabilities
- Brian McNoldy Atlantic Headquarters
- Brian McNoldy Tropical Satellite Sectors
- Brian McNoldy Infrared Hovmoller
- Brian McNoldy Past TC Radar Loops
- Weather Nerds TC Guidance
- Twister Data Model Guidance
- NOAA Tropical Cyclone Tracks
- Albany GFS/ EURO Models/ Ensembles
- Albany Tropical Cyclone Guidance
- Albany Tropical Atlantic Model Maps
- Pivotal Weather Model Guidance
- Weather Online Model Guidance
- UKMet Model Guidance/ Analysis/ Sat
- ECMWF (EURO) Model Guidance
- FSU Tropical Model Outputs
- FSU Tropical Cyclone Genesis
- Penn State Tropical E-Wall
- NOAA HFIP Ruc Models
- Navy NRL TC Page
- College of DuPage Model Guidance
- WXCharts Model Guidance
- NOAA NHC Analysis Tools
- NOAA NHC ATCF Directory
- NOAA NCEP/EMC Cyclogenesis Tracking
- NOAA NCEP/EMC HWRF Model
- NOAA HFIP Model Products
- University of Miami Ocean Heat
- COLA Max Potential Hurricane Intensity
- Colorado State RAMMB TC Tracking
- Colorado State RAMMB Floaters
- Colorado State RAMMB GOES-16 Viewer
- NOAA NESDIS GOES Satellite
- ASCAT Ocean Surface Winds METOP-A
- ASCAT Ocean Surface Winds METOP-B
- Michael Ventrice Waves / MJO Maps
- TropicalAtlantic.com Analysis / Recon
- NCAR/RAL Tropical Cyclone Guidance
- CyclonicWX Tropical Resources
Historic Louisiana Storms By Month
January
June
July
August
September
October
Impacts of El Niño and La Niña (ENSO) on Hurricane Season
First it is important to know El Niño and La Niña are part of a single climate phenomenon called ENSO, it has three states, or phases, it can be in. The two opposite phases, “El Niño” and “La Niña,” require certain changes in both the ocean and the atmosphere because ENSO is a coupled climate phenomenon. “Neutral” is in the middle of the continuum.
The effect that El Niño and La Niña have on both the Atlantic and Pacific hurricane seasons is worth exploring. The hurricane impacts of El Niño and its counterpart La Niña are like a see-saw between the Pacific and Atlantic oceans, strengthening hurricane activity in one region while weakening it in the other. Great graphics below explain these effects.
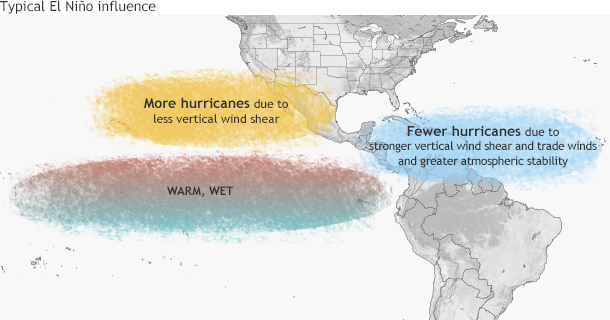 Typical influence of El Niño on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
Simply put, El Niño favors stronger hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and suppresses it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 1). Conversely, La Niña suppresses hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and enhances it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 2).
Typical influence of El Niño on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
Simply put, El Niño favors stronger hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and suppresses it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 1). Conversely, La Niña suppresses hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and enhances it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 2).
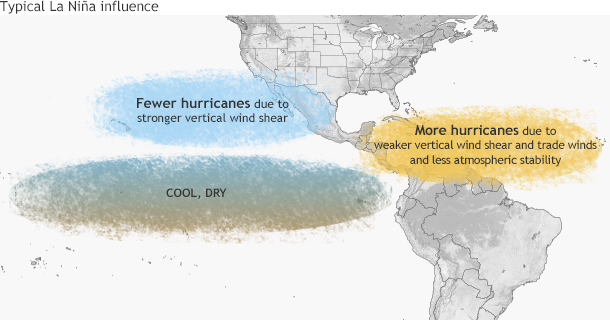 Typical influence of La Niña on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
These impacts are primarily caused by changes in the vertical wind shear, which refers to the change in wind speed and direction between roughly 5,000-35,000 ft. above the ground. Strong vertical wind shear can rip a developing hurricane apart, or even prevent it from forming.
ENSO perturbs tropical and subtropical atmospheric circulation
During El Niño, the area of tropical Pacific convection and its associated Hadley circulation expand eastward from the western Pacific, sometimes extending to the west coast of South America. (A tutorial on El Niño and La Niña can be found at the NOAA Climate Prediction Center website.) At the same time, the equatorial Walker circulation is weaker than average.
These conditions produce an anomalous upper-level, ridge-trough pattern in the subtropics, with an amplified ridge over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the enhanced convection, and a downstream trough over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern Pacific, the enhanced subtropical ridge is associated with weaker upper-level winds and reduced vertical wind shear, which favors more hurricane activity.
Over the Atlantic basin, the amplified trough is associated with stronger upper-level westerly winds and stronger lower-level easterly trade winds, both of which increase the vertical wind shear and suppress hurricane activity. In addition to enhanced vertical wind shear, El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing the amount of sinking motion and increasing the atmospheric stability.
La Niña has opposite impacts across the Pacific and Atlantic basins. During La Niña, the area of tropical convection and its Hadley circulation is retracted westward to the western Pacific and Indonesia, and the equatorial Walker circulation is enhanced. Convection is typically absent across the eastern half of the equatorial Pacific.
In the upper atmosphere, these conditions produce an amplified trough over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the suppressed convection, and a downstream ridge over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern subtropical Pacific, the enhanced trough is associated with stronger upper-level winds and stronger vertical wind shear, which suppress hurricane activity. Over the Atlantic basin, the anomalous upper-level ridge is associated with weaker upper- and lower- level winds, both of which reduce the vertical wind shear and increased hurricane activity. La Niña also favors increased Atlantic hurricane activity by decreasing the amount of sinking motion and decreasing the atmospheric stability.
Credit and more information found at: Climate.gov
More information on ENSO and other impacts of this phenomenon:
What is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in a nutshell?
ENSO Status and Impacts
Typical influence of La Niña on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
These impacts are primarily caused by changes in the vertical wind shear, which refers to the change in wind speed and direction between roughly 5,000-35,000 ft. above the ground. Strong vertical wind shear can rip a developing hurricane apart, or even prevent it from forming.
ENSO perturbs tropical and subtropical atmospheric circulation
During El Niño, the area of tropical Pacific convection and its associated Hadley circulation expand eastward from the western Pacific, sometimes extending to the west coast of South America. (A tutorial on El Niño and La Niña can be found at the NOAA Climate Prediction Center website.) At the same time, the equatorial Walker circulation is weaker than average.
These conditions produce an anomalous upper-level, ridge-trough pattern in the subtropics, with an amplified ridge over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the enhanced convection, and a downstream trough over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern Pacific, the enhanced subtropical ridge is associated with weaker upper-level winds and reduced vertical wind shear, which favors more hurricane activity.
Over the Atlantic basin, the amplified trough is associated with stronger upper-level westerly winds and stronger lower-level easterly trade winds, both of which increase the vertical wind shear and suppress hurricane activity. In addition to enhanced vertical wind shear, El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing the amount of sinking motion and increasing the atmospheric stability.
La Niña has opposite impacts across the Pacific and Atlantic basins. During La Niña, the area of tropical convection and its Hadley circulation is retracted westward to the western Pacific and Indonesia, and the equatorial Walker circulation is enhanced. Convection is typically absent across the eastern half of the equatorial Pacific.
In the upper atmosphere, these conditions produce an amplified trough over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the suppressed convection, and a downstream ridge over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern subtropical Pacific, the enhanced trough is associated with stronger upper-level winds and stronger vertical wind shear, which suppress hurricane activity. Over the Atlantic basin, the anomalous upper-level ridge is associated with weaker upper- and lower- level winds, both of which reduce the vertical wind shear and increased hurricane activity. La Niña also favors increased Atlantic hurricane activity by decreasing the amount of sinking motion and decreasing the atmospheric stability.
Credit and more information found at: Climate.gov
More information on ENSO and other impacts of this phenomenon:
What is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in a nutshell?
ENSO Status and Impacts
 Typical influence of El Niño on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
Simply put, El Niño favors stronger hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and suppresses it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 1). Conversely, La Niña suppresses hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and enhances it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 2).
Typical influence of El Niño on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
Simply put, El Niño favors stronger hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and suppresses it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 1). Conversely, La Niña suppresses hurricane activity in the central and eastern Pacific basins, and enhances it in the Atlantic basin (Figure 2).
 Typical influence of La Niña on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
These impacts are primarily caused by changes in the vertical wind shear, which refers to the change in wind speed and direction between roughly 5,000-35,000 ft. above the ground. Strong vertical wind shear can rip a developing hurricane apart, or even prevent it from forming.
ENSO perturbs tropical and subtropical atmospheric circulation
During El Niño, the area of tropical Pacific convection and its associated Hadley circulation expand eastward from the western Pacific, sometimes extending to the west coast of South America. (A tutorial on El Niño and La Niña can be found at the NOAA Climate Prediction Center website.) At the same time, the equatorial Walker circulation is weaker than average.
These conditions produce an anomalous upper-level, ridge-trough pattern in the subtropics, with an amplified ridge over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the enhanced convection, and a downstream trough over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern Pacific, the enhanced subtropical ridge is associated with weaker upper-level winds and reduced vertical wind shear, which favors more hurricane activity.
Over the Atlantic basin, the amplified trough is associated with stronger upper-level westerly winds and stronger lower-level easterly trade winds, both of which increase the vertical wind shear and suppress hurricane activity. In addition to enhanced vertical wind shear, El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing the amount of sinking motion and increasing the atmospheric stability.
La Niña has opposite impacts across the Pacific and Atlantic basins. During La Niña, the area of tropical convection and its Hadley circulation is retracted westward to the western Pacific and Indonesia, and the equatorial Walker circulation is enhanced. Convection is typically absent across the eastern half of the equatorial Pacific.
In the upper atmosphere, these conditions produce an amplified trough over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the suppressed convection, and a downstream ridge over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern subtropical Pacific, the enhanced trough is associated with stronger upper-level winds and stronger vertical wind shear, which suppress hurricane activity. Over the Atlantic basin, the anomalous upper-level ridge is associated with weaker upper- and lower- level winds, both of which reduce the vertical wind shear and increased hurricane activity. La Niña also favors increased Atlantic hurricane activity by decreasing the amount of sinking motion and decreasing the atmospheric stability.
Credit and more information found at: Climate.gov
More information on ENSO and other impacts of this phenomenon:
What is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in a nutshell?
ENSO Status and Impacts
Typical influence of La Niña on Pacific and Atlantic seasonal hurricane activity. Map by NOAA Climate.gov, based on originals by Gerry Bell.
These impacts are primarily caused by changes in the vertical wind shear, which refers to the change in wind speed and direction between roughly 5,000-35,000 ft. above the ground. Strong vertical wind shear can rip a developing hurricane apart, or even prevent it from forming.
ENSO perturbs tropical and subtropical atmospheric circulation
During El Niño, the area of tropical Pacific convection and its associated Hadley circulation expand eastward from the western Pacific, sometimes extending to the west coast of South America. (A tutorial on El Niño and La Niña can be found at the NOAA Climate Prediction Center website.) At the same time, the equatorial Walker circulation is weaker than average.
These conditions produce an anomalous upper-level, ridge-trough pattern in the subtropics, with an amplified ridge over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the enhanced convection, and a downstream trough over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern Pacific, the enhanced subtropical ridge is associated with weaker upper-level winds and reduced vertical wind shear, which favors more hurricane activity.
Over the Atlantic basin, the amplified trough is associated with stronger upper-level westerly winds and stronger lower-level easterly trade winds, both of which increase the vertical wind shear and suppress hurricane activity. In addition to enhanced vertical wind shear, El Niño suppresses Atlantic hurricane activity by increasing the amount of sinking motion and increasing the atmospheric stability.
La Niña has opposite impacts across the Pacific and Atlantic basins. During La Niña, the area of tropical convection and its Hadley circulation is retracted westward to the western Pacific and Indonesia, and the equatorial Walker circulation is enhanced. Convection is typically absent across the eastern half of the equatorial Pacific.
In the upper atmosphere, these conditions produce an amplified trough over the subtropical Pacific in the area north of the suppressed convection, and a downstream ridge over the Caribbean Sea and western tropical Atlantic. Over the central and eastern subtropical Pacific, the enhanced trough is associated with stronger upper-level winds and stronger vertical wind shear, which suppress hurricane activity. Over the Atlantic basin, the anomalous upper-level ridge is associated with weaker upper- and lower- level winds, both of which reduce the vertical wind shear and increased hurricane activity. La Niña also favors increased Atlantic hurricane activity by decreasing the amount of sinking motion and decreasing the atmospheric stability.
Credit and more information found at: Climate.gov
More information on ENSO and other impacts of this phenomenon:
What is the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) in a nutshell?
ENSO Status and Impacts

 DONATE
DONATE