SUPPORT TRACK THE TROPICS
Over the last decade plus if you appreciate the information and tracking I provide during the season along with this website which donations help keep it running please consider a one time... recurring or yearly donation if you are able to help me out...
Venmo: @TrackTheTropicsLouisiana
Website: TrackTheTropics.com/DONATE
Venmo: @TrackTheTropicsLouisiana
Website: TrackTheTropics.com/DONATE
Track The Tropics is the #1 source to track the tropics 24/7! Since 2013 the main goal of the site is to bring all of the important links and graphics to ONE PLACE so you can keep up to date on any threats to land during the Atlantic Hurricane Season! Hurricane Season 2026 in the Atlantic starts on June 1st and ends on November 30th. Do you love Spaghetti Models? Well you've come to the right place!! Remember when you're preparing for a storm: Run from the water; hide from the wind!
Tropical Atlantic Weather Resources
- NOAA National Hurricane Center
- International Meteorology Database
- FSU Tropical Cyclone Track Probabilities
- Brian McNoldy Atlantic Headquarters
- Brian McNoldy Tropical Satellite Sectors
- Brian McNoldy Infrared Hovmoller
- Brian McNoldy Past TC Radar Loops
- Weather Nerds TC Guidance
- Twister Data Model Guidance
- NOAA Tropical Cyclone Tracks
- Albany GFS/ EURO Models/ Ensembles
- Albany Tropical Cyclone Guidance
- Albany Tropical Atlantic Model Maps
- Pivotal Weather Model Guidance
- Weather Online Model Guidance
- UKMet Model Guidance/ Analysis/ Sat
- ECMWF (EURO) Model Guidance
- FSU Tropical Model Outputs
- FSU Tropical Cyclone Genesis
- Penn State Tropical E-Wall
- NOAA HFIP Ruc Models
- Navy NRL TC Page
- College of DuPage Model Guidance
- WXCharts Model Guidance
- NOAA NHC Analysis Tools
- NOAA NHC ATCF Directory
- NOAA NCEP/EMC Cyclogenesis Tracking
- NOAA NCEP/EMC HWRF Model
- NOAA HFIP Model Products
- University of Miami Ocean Heat
- COLA Max Potential Hurricane Intensity
- Colorado State RAMMB TC Tracking
- Colorado State RAMMB Floaters
- Colorado State RAMMB GOES-16 Viewer
- NOAA NESDIS GOES Satellite
- ASCAT Ocean Surface Winds METOP-A
- ASCAT Ocean Surface Winds METOP-B
- Michael Ventrice Waves / MJO Maps
- TropicalAtlantic.com Analysis / Recon
- NCAR/RAL Tropical Cyclone Guidance
- CyclonicWX Tropical Resources
Historic Louisiana Storms By Month
January
June
July
August
September
October
Tropical Cyclones 101
Index
- Tropical Cyclones 101
- Tropical Cyclone Classification
- Tropical Cyclone Structure
- Tropical Cyclone Names
- Tropical Cyclone Hazards
- Hurricane Damage Potential
- Tropical Cyclone Safety
Introduction
 A tropical cyclone is a warm-core, low pressure system without any "front" attached, that develops over the tropical or subtropical waters, and has an organized circulation. Depending upon location, tropical cyclones have different names around the world. In the:
A tropical cyclone is a warm-core, low pressure system without any "front" attached, that develops over the tropical or subtropical waters, and has an organized circulation. Depending upon location, tropical cyclones have different names around the world. In the:
- Atlantic/Eastern Pacific Oceans - hurricanes
- Western Pacific - typhoons
- Indian Ocean - cyclones
- Warm ocean waters (at least 80°F / 27°C) throughout a depth of about 150 ft. (46 m).
- An atmosphere which cools fast enough with height such that it is potentially unstable to moist convection.
- Relatively moist air near the mid-level of the troposphere (16,000 ft. / 4,900 m).
- Generally a minimum distance of at least 300 miles (480 km) from the equator.
- A pre-existing near-surface disturbance.
- Low values (less than about 23 mph / 37 km/h) of vertical wind shear between the surface and the upper troposphere. Vertical wind shear is the change in wind speed with height.
Tropical Cyclone Formation Basin
Formation and movement of Tropical Cyclones 1945-2006
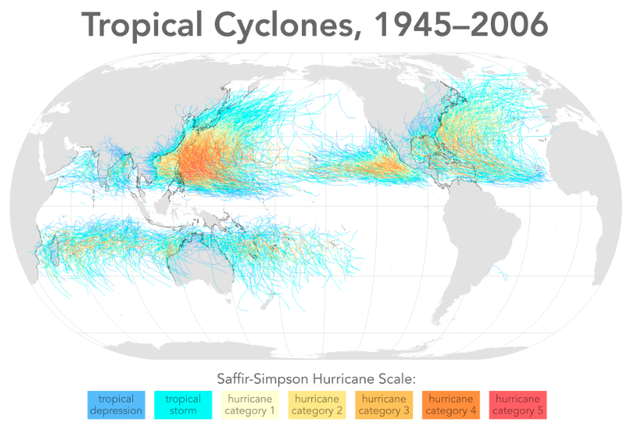
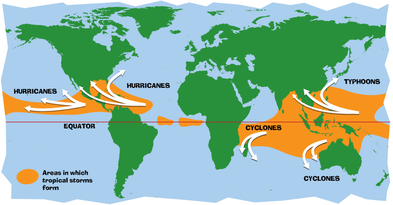 Given that sea surface temperatures need to be at least 80°F (27°C) for tropical cyclones form, it is natural that they form near the equator. However, with only the rarest of occasions, these storms do not form within 5° latitude of the equator. This is due to the lack of sufficient Coriolis Force, the force that causes the cyclone to spin. However, tropical cyclones form in seven regions around the world.
See the probabilities for the Atlantic Basin by month.
One rare exception to the lack of tropical cyclones near the equator was Typhoon Vamei which former near Singapore on December 27, 2001. Since tropical cyclone observations started in 1886 in the North Atlantic and 1945 in the western North Pacific, the previous recorded lowest latitude for a tropical cyclone was 3.3°N for Typhoon Sarah in 1956. With its circulation center at 1.5°N Typhoon Vamei's circulation was on both sides of the equator. U.S. Naval ships reported maximum sustained surface wind of 87 mph and gust wind of up to 120 mph.
Given that sea surface temperatures need to be at least 80°F (27°C) for tropical cyclones form, it is natural that they form near the equator. However, with only the rarest of occasions, these storms do not form within 5° latitude of the equator. This is due to the lack of sufficient Coriolis Force, the force that causes the cyclone to spin. However, tropical cyclones form in seven regions around the world.
See the probabilities for the Atlantic Basin by month.
One rare exception to the lack of tropical cyclones near the equator was Typhoon Vamei which former near Singapore on December 27, 2001. Since tropical cyclone observations started in 1886 in the North Atlantic and 1945 in the western North Pacific, the previous recorded lowest latitude for a tropical cyclone was 3.3°N for Typhoon Sarah in 1956. With its circulation center at 1.5°N Typhoon Vamei's circulation was on both sides of the equator. U.S. Naval ships reported maximum sustained surface wind of 87 mph and gust wind of up to 120 mph.
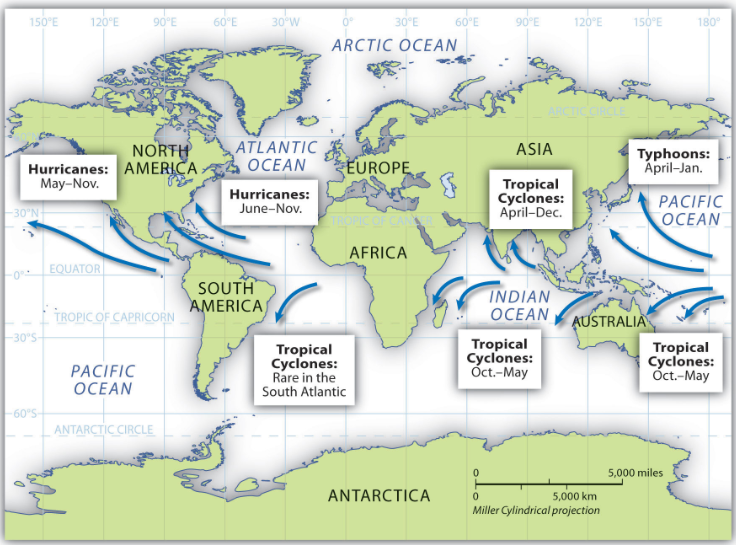 The seedlings of tropical cyclones, called "disturbances", can come from:
The seedlings of tropical cyclones, called "disturbances", can come from:
- Easterly Waves: Also called tropical waves, this is an inverted trough of low pressure moving generally westward in the tropical easterlies. A trough is defined as a region of relative low pressure. The majority of tropical cyclones form from easterly waves.
- West African Disturbance Line (WADL): This is a line of convection (similar to a squall line) which forms over West Africa and moves into the Atlantic Ocean. WADL's usually move faster than tropical waves.
- TUTT: A TUTT (Tropical Upper Tropospheric Trough) is a trough, or cold core low in the upper atmosphere, which produces convection. On occasion, one of these develops into a warm-core tropical cyclone.
- Old Frontal Boundary: Remnants of a polar front can become lines of convection and occasionally generate a tropical cyclone. In the Atlantic Ocean storms, this will occur early or late in the hurricane season in the Gulf of Mexico or Caribbean Sea.
 The NASA image (left) is Hurricane Wilma in October 2005. Clicking the image will load a 8mb movie (provided by NASA) showing the life of the storm. The color of the ocean represents sea surface temperature with orange and red colors indicating temperatures of 82°F or greater.
As Wilma moves northwest, then eventually northeast, the water temperature decreases (indicated by the change to light blue color) after the storm passes a particular location. This is the result of the heat that is removed from the ocean and provided to the storm.
Therein shows the purpose of tropical cyclones. Their role is to take heat, stored in the ocean, and transfer it to the upper atmosphere where the upper level winds carry that heat to the poles. This keeps the polar regions from being as cold as they could be and helps keep the tropics from overheating.
There are many suggestions for the mitigation of tropical cyclones such as "seeding" storms with chemicals to decrease their intensity, dropping water absorbing material into the storm to soak-up some of the moisture, to even using nuclear weapons to disrupt their circulation thereby decreasing their intensity. Read about tropical cyclone myths. While well meaning, the ones making the suggestions vastly underestimate the amount of energy generated and released by tropical cyclones.
Even if we could disrupt these storms, it would not be advisable. Since tropical cyclones help regulate the earth's temperature, any decrease in tropical cyclone intensity means the oceans retain more heat. Over time, the build-up of heat could possible enhance subsequent storms and lead to more numerous and/or stronger events.
There has also been much discussion about the abnormally high number of storms for the 2005 Atlantic basin (27 named storms including 15 hurricanes). Compared to the age of the earth, our knowledge about tropical cyclone history is only very recent. Only since the advent of satellite imagery in the 1960's do we have any real ability to count, track and observe these systems across the vast oceans. Therefore, we will never know the actual record number of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Oceans.
The NASA image (left) is Hurricane Wilma in October 2005. Clicking the image will load a 8mb movie (provided by NASA) showing the life of the storm. The color of the ocean represents sea surface temperature with orange and red colors indicating temperatures of 82°F or greater.
As Wilma moves northwest, then eventually northeast, the water temperature decreases (indicated by the change to light blue color) after the storm passes a particular location. This is the result of the heat that is removed from the ocean and provided to the storm.
Therein shows the purpose of tropical cyclones. Their role is to take heat, stored in the ocean, and transfer it to the upper atmosphere where the upper level winds carry that heat to the poles. This keeps the polar regions from being as cold as they could be and helps keep the tropics from overheating.
There are many suggestions for the mitigation of tropical cyclones such as "seeding" storms with chemicals to decrease their intensity, dropping water absorbing material into the storm to soak-up some of the moisture, to even using nuclear weapons to disrupt their circulation thereby decreasing their intensity. Read about tropical cyclone myths. While well meaning, the ones making the suggestions vastly underestimate the amount of energy generated and released by tropical cyclones.
Even if we could disrupt these storms, it would not be advisable. Since tropical cyclones help regulate the earth's temperature, any decrease in tropical cyclone intensity means the oceans retain more heat. Over time, the build-up of heat could possible enhance subsequent storms and lead to more numerous and/or stronger events.
There has also been much discussion about the abnormally high number of storms for the 2005 Atlantic basin (27 named storms including 15 hurricanes). Compared to the age of the earth, our knowledge about tropical cyclone history is only very recent. Only since the advent of satellite imagery in the 1960's do we have any real ability to count, track and observe these systems across the vast oceans. Therefore, we will never know the actual record number of tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Oceans.

 DONATE
DONATE